Blog | 2025/08/10
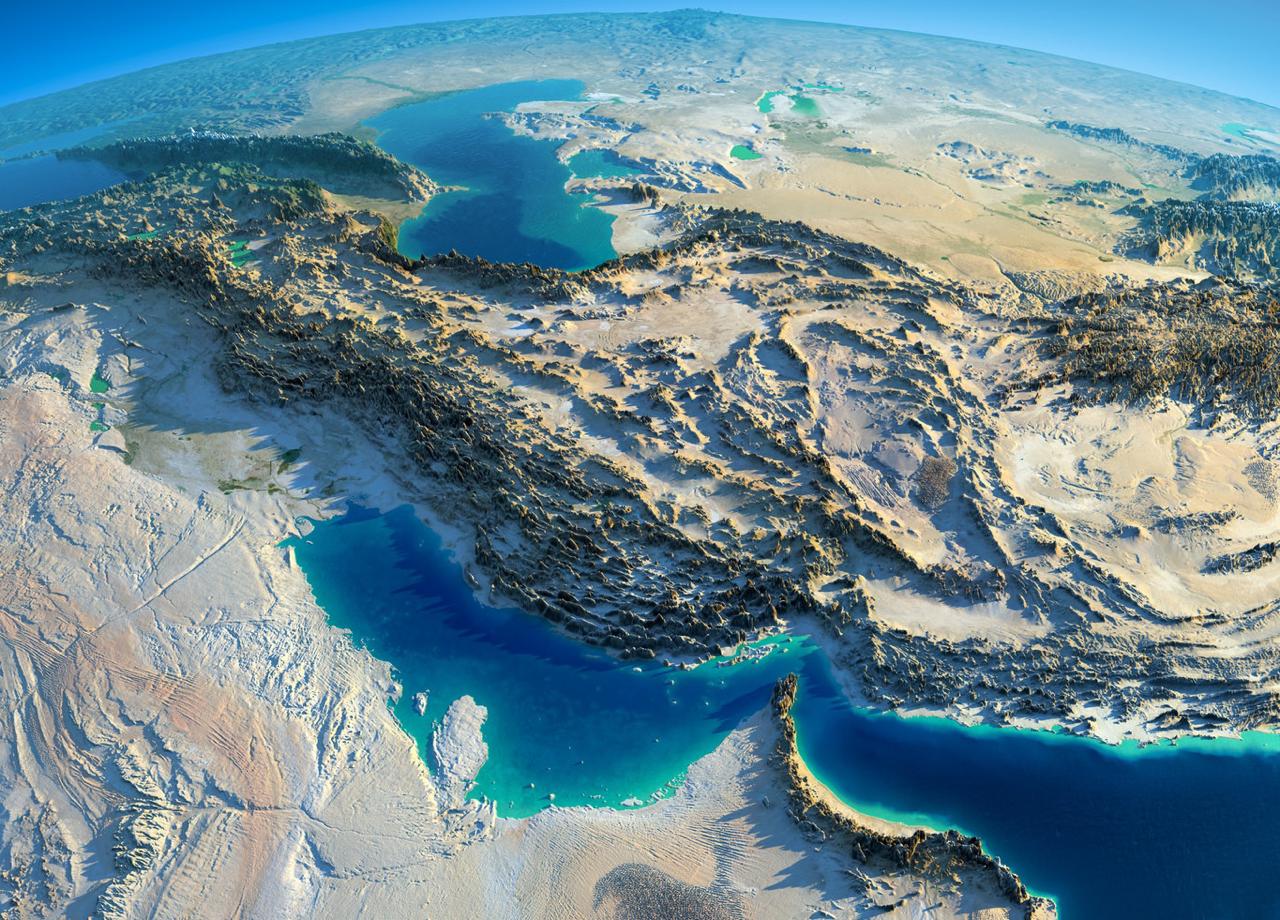
Iran, with an area of 1,648,195 square kilometers, is located in Southwest Asia. Geographically, it lies between 25 to 45 degrees north latitude and 40 to 63 degrees east longitude, bordered by Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan and Armenia to the north, Turkey and Iraq to the west, Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea to the south.
The Iranian plateau is part of the Alp-Himalayan mountain belt and includes three main regions: the Alborz mountain range in the north with Mount Damavand (Iran's highest peak at 5,610 meters), the Zagros mountains in the west, and the central plateau which includes vast plains and deserts. The country's average elevation is about 1,250 meters above sea level.


Iran has significant climatic diversity. The northern region has a moderate Caspian climate with annual rainfall up to 2,000 mm, while the central regions have a semi-arid climate with less than 200 mm of precipitation. The southern and eastern areas have a hot and dry climate with high temperatures and intense evaporation. The Alborz and Zagros mountain ranges have a mountainous climate with cold winters and mild summers.
Regarding topography, mountains cover about 55% of Iran's area, including the Alborz, Zagros and central mountain ranges. The remaining 45% consists of plains and lowlands such as the fertile Khuzestan plain, Dasht-e Kavir and Lake Urmia. Main water resources include the Karun, Sefidrud and Zayandeh rivers and lakes such as Urmia and Hamun.






Blog | 2025/05/17

Blog | 2025/05/17

Blog | 2025/05/17
.jpg)
Blog | 2025/05/14


